IBM QRadar vs. Splunk SIEM
What are SIEM and SOC?
Security information and event management (SIEM) is the process of real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware, which is done by incorporating SIM and SEM under one framework. The machine-generated data is collected and monitored for security assessment.
SOC or the Security Operations Center is a facility that houses a team of security experts that monitors the organization’s security and safeguards it. The SOC includes various sectors like SIEM, GRC, VAPT tools, IDS, and IPS. SIEM is an integral part of the Security Operation Center (SOC).

We will discuss two SIEM products here: Splunk and IBM QRadar.
Key Factors of Comparison
- History of Products
- Gartner’s Magic Quadrant 2020
- Deployment & Target Industry
- Fundamental Comparison (Pricing, metrics, and Intelligence)
- Pros and cons of Splunk
- Pros and Cons of IBM QRadar
- 1. History of Products
Splunk: Splunk was founded in 2003, becoming the world’s first, in the words of Splunk founders- “A Data-to-everything Platform,” designed to bridge the gap between data and security by introducing the intelligent data monitoring system.
QRadar: Qradar was developed by Q1 Labs and acquired by IBM in 2011. IBM announced that the acquisition would help its clients more intelligently secure their organization by applying analytics to connect information from major security domains and forming security dashboards for their organizations.
- 2. Gartner’s Magic Quadrant 2020:
Gartner is a prominent research and advisory company which has clients in 77% of the worlds’ top 500 companies of all size. They release their research on the various domain of information security and Information technology on an annual basis, and we’re considering one such annual summary. The image under discussion is the Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for the year 2020 under the category of SIEM (Security Information and Event Management).
The quadrant is divided into four sections:
- 1. Challengers
- 2. Leaders
- 3. Niche Players, and
- 4. Visionaries
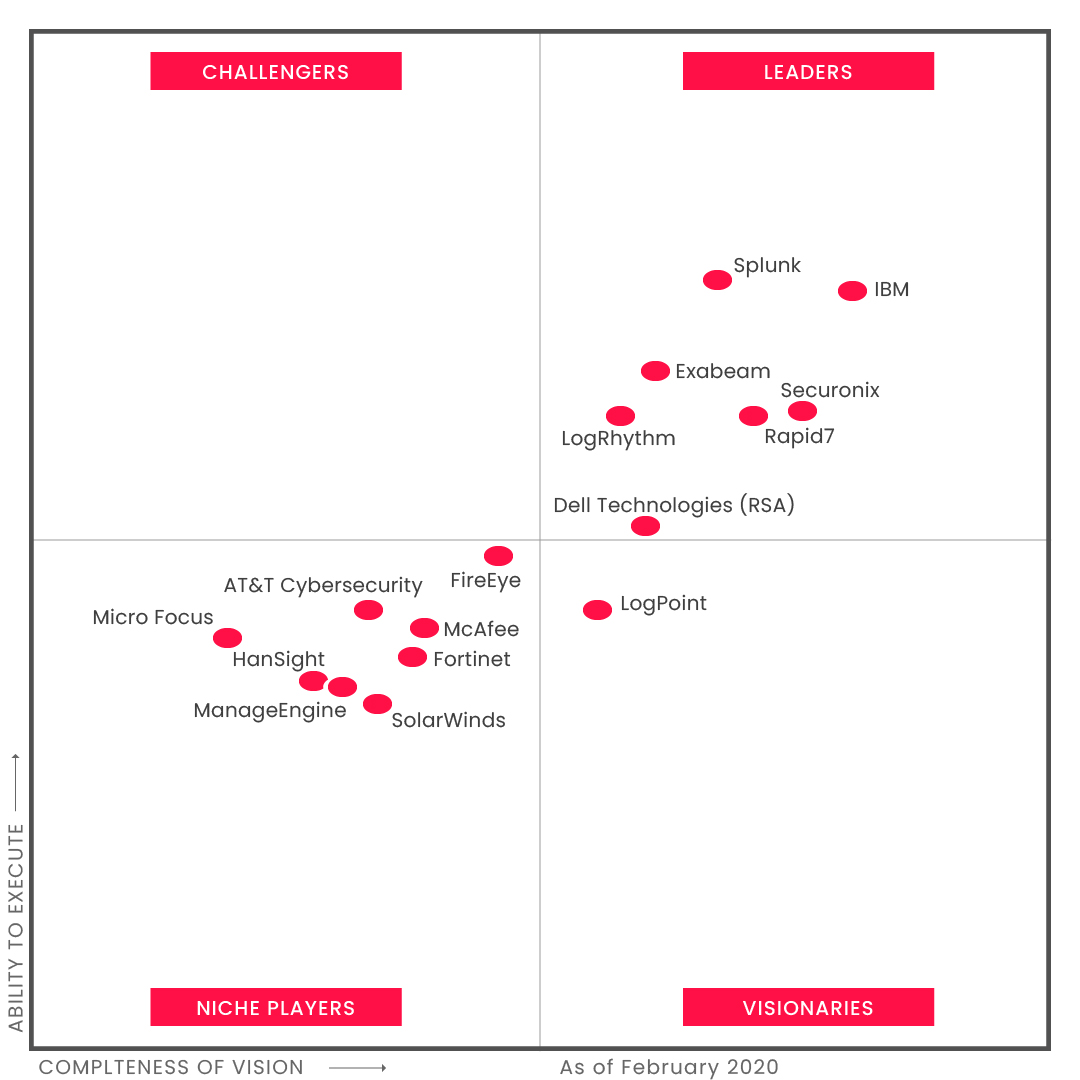
Gartner investigates various SIEM products on the basis of key attributes of comparison and importance and summarizes their report in the form of Magic Quadrant and Critical Capabilities.
Some of the attributes that Gartner evaluates the products are:
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Threat Intelligence
- Analytics
- Reviewer Demographics by reviewer and company size
Below are the attributes used in QRadar v/s Splunk for this year.
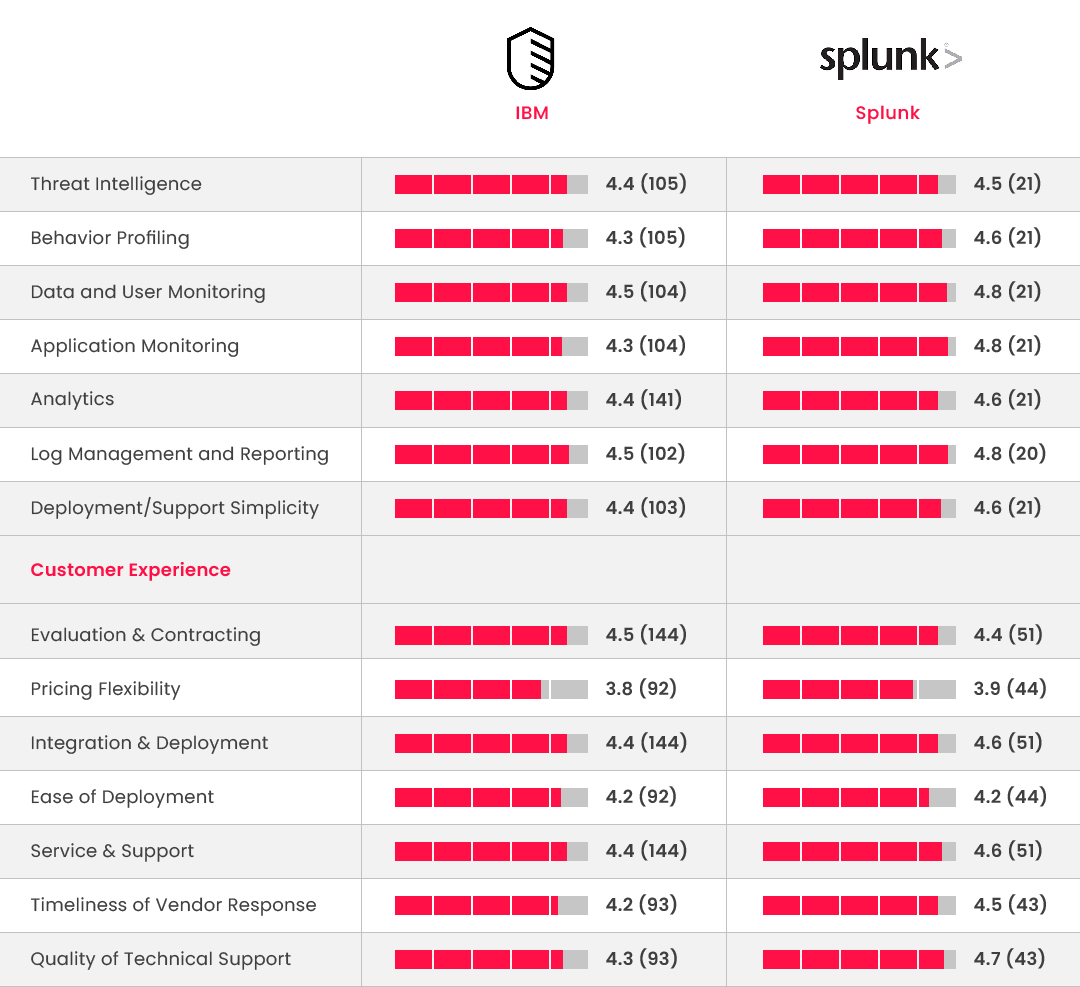
3. Deployment & Target Industry
Splunk: Splunk is primarily developed to be deployed as a software on-premise as a SaaS solution on Splunk cloud. It can also be deployed on public or private cloud and even Hybrid cloud (a combination of private and public cloud)
Splunk is essentially used for industries that are heavily regulated. E.g., Oil and Gas, Financial services, healthcare, Banks, Airline and Railways, nuclear plants, space research organizations, etc.
QRadar: QRadar is available as on-premises hardware or software or in the cloud. Smaller customers can offload all the deployment and maintenance to an IBM cloud-based solution, while larger firms can choose either an on-premises deployment or adopt a hybrid approach collecting data from local and cloud-based applications
QRadar is used in enterprises and moderately regulated industries. E.g., Private IT corporations, small to large companies.
4. Fundamental Comparison (Pricing, metrics, and Intelligence)
We’ve seen that QRadar is used in Medium to Large organizations, and Splunk is deployed in small-scale enterprises. We’ll see some detailed analysis of both these products based on:
- Pricing
- Metrics
- Intelligence
We’ll discuss these components for Splunk and QRadar:
- 1. Splunk:
- Metric: Based on the number of users & amount of data ingested per day. (Several petabytes/day)
- Intelligence: Integrates with Splunk User Behaviour Analysis (UBA) and Machine Learning Toolkit.
- Pricing: Based on max daily data volume, Starting at $1,800/GB/day.
- 2. QRadar:
- Metric: Based on Events Per Second (EPS) and Flows Per Second (FPS).
- Intelligence: Ideal for UBA, IBM Watson, and packet inspection.
- Pricing: Cloud: $800/month On premise: $10,400
5. Pros and cons of Splunk
After going over the basic comparison between the two, here are some insightful findings:
- Pros:
- 1. Easiest to get any sets of data using the rich UI and APIs.
- 2. Splunk Stream can collect network traffic for analysis, and the Splunk Universal Forwarder can be used as a lightweight agent for endpoint analysis.
- 3. This advanced technology has the edge over its competitors by providing real-time data processing, which has been achieved due to the advancement in the processors and hardware of devices.
- Cons:
- 1. Splunk is not an open-source technology
- 2. The overall cost of implementation is initially high.
6. Pros and Cons of IBM QRadar
- Pros:
- 1. Excellent fit for the midsize to large enterprises that require SIEM as well as those seeking a unified dashboard for managing a wide range of security monitoring.
- 2. One of its kind sets of functions which help the user to manage their logs efficiently (Application, compliance, network overview, risk, system & threat monitoring)
- Cons:
- 1. The UBA of Splunk is far superior to the one provided by QRadar. Thus, making QRadar lag behind in the market.
- 2. Workflow and incident response and management capabilities are better than average, but full potential and automation can be achieved only by opting for IBM’s Resilient Incident Response Platform premium solution.
MacAfee ESM and AlienVault USM are major competitors of QRadar apart from Splunk.
SOC Analyst training with Infosec Train
Infosec Train has recently introduced its custom-designed SOC analyst training program to help to aspire and current SOC analysts. The training program aims at providing the necessary skills to the L1, L2, and L3 SOC analysts. Check out the course content and the latest schedule of our SOC analyst training program:
Infosec Train’s SOC Analyst Expert Training
Get yourself enrolled in our IBM Security QRadar training and get hands-on experience in administering, managing, and tuning the IBM QRadar SIEM solution.
Infosec Train’s IBM Security QRadar SIEM Training





 1800-843-7890 (IN)
1800-843-7890 (IN) sales@infosectrain.com
sales@infosectrain.com
 1800-843-7890 (India)
1800-843-7890 (India) 
