CCSP Domain 3: Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security
CCSP
The Certified Cloud Security Professional Certification, or CCSP, is a joint certification from (ISC)2 and the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA). The CCSP credential was launched in 2015 for security professionals whose daily responsibilities include procuring, protecting, and managing cloud environments or acquired cloud services. The CCSP is a good certificate to get for information security practitioners who want to specialize in cloud computing security. It was developed by (ISC)2 to ensure that cloud security professionals have the knowledge, skills, and ability to design, implement, architect, operate, control, and enforce regulatory frameworks. (ISC)2 is a non-profit membership organization dedicated to encouraging a safe and secure cyber environment. By bringing information security skills to a cloud computing environment, a CCSP exhibits proficiency in cloud security architecture, design, operation, and service orchestration. This professional knowledge is compared to a widely accepted body of information.
The CCSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK) covers a wide range of topics, making it relevant to all aspects of cloud security. Six domains are included in the CCSP exam:
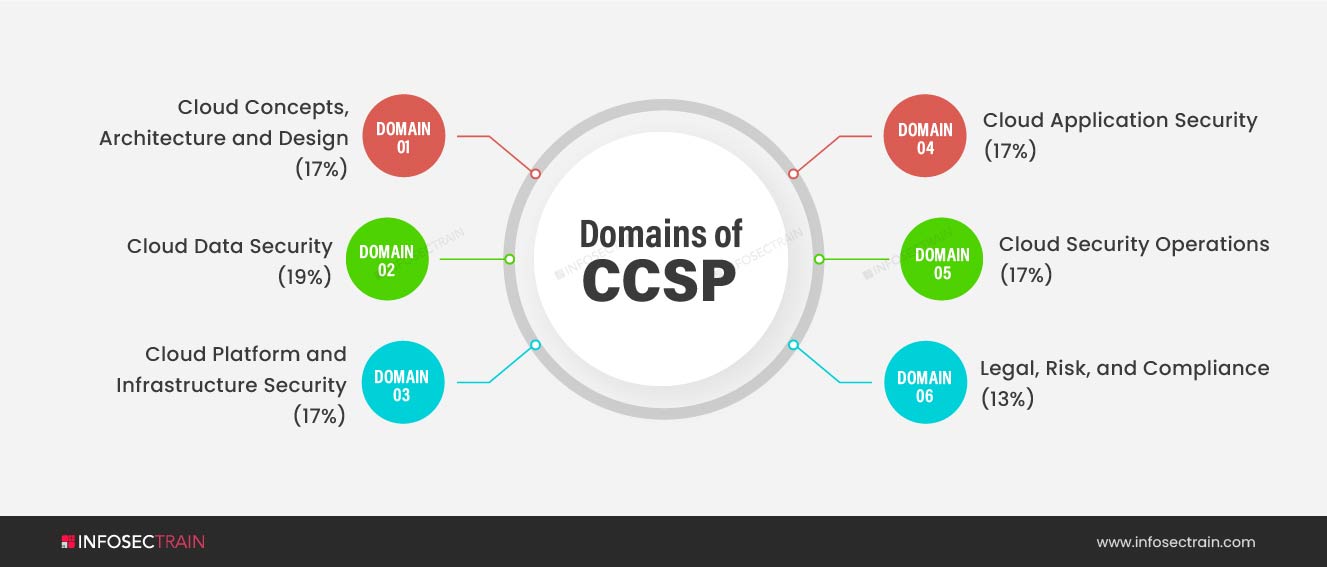
- Domain 1: Cloud Concepts, Architecture and Design (17%)
- Domain 2: Cloud Data Security (19%)
- Domain 3: Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security (17%)
- Domain 4: Cloud Application Security (17%)
- Domain 5: Cloud Security Operations (17%)
- Domain 6: Legal, Risk, and Compliance (13%)
This blog will discuss CCSP Domain 3: Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security, as well as what you should expect in this domain when preparing for the exam.
Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security
The third domain of CCSP focuses on cloud infrastructure security. A CCSP candidate should understand the fundamental components of cloud architecture, must be able to perform a risk assessment, design and implement cloud security measures, and understand how to integrate cloud computing into their company’s business continuity/disaster recovery (BC/DR) plan. The domain has a weightage of 17% and covers the following topics:
- Comprehend Cloud Infrastructure Components
- Design a Secure Data Center
- Analyze Risks Associated with Cloud Infrastructure
- Design and Plan Security Controls
- Plan Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC)
To know more about CCSP 3rd domain exam outline in-depth you can refer to the below link:
Below is a breakdown of the various subsections of this domain and what you may expect to see on the CCSP certification exam.
Comprehend Cloud Infrastructure Components
A cloud environment comprises both physical and virtual infrastructure, with its own set of security problems and requirements. While cloud systems are built on virtualization and virtual components, the actual hardware and its security requirements are present beneath those virtualization layers, just as they are in a traditional data center. Many of the same components that make up a traditional data center are used in the cloud infrastructure, but with a different perspective.
Design a Secure Data Center
The cloud infrastructure is housed in data centers, which are physical environments. This subsection covers physical systems, such as BIOS and hardware layers, as well as software that hosts and maintains virtualized environments on top of them. Any physical layer security or control breach might put any virtual hosts managed within it in jeopardy. The standard set of resources in a cloud environment: network and communications, storage, and computing are all subject to security measures. Virtualization, on the other hand, necessitates security considerations in terms of the management plane that controls the virtual machines.
Analyze Risks Associated with Cloud Infrastructure
This section explores cloud-specific risks, virtualization-related risks, and specialized countermeasure solutions. Risks associated with cloud-based systems are similar to those associated with traditional hosting models, with the addition of risks particular to cloud hosting. A cloud-based system should be treated and maintained in the same way that any other outsourced platform is, with the same issues, risks, and audit/governance needs. All businesses must regularly assess the risks to all systems, applications, and data, as well as management’s risk appetite and risk tolerance.
Design and Plan Security Controls
The Cloud Security Professional should concentrate on numerous distinct areas to guarantee a sound security policy and overall governance. Because cloud computing is commonly utilized to connect organizations and provide services to large numbers and groups of users, identity and access management is a crucial idea for the Cloud Security Professional to comprehend. The proper identification of users and the security measures usually used to authenticate and establish their identity to satisfy policy or regulatory requirements are covered. Once a user’s identity has been verified, strict authorization controls are required to ensure that they only access information for which they have been granted access and through the means for which they have been granted access. Federated identity is a common approach with many cloud-based systems, in which users authenticate through their own organization’s identity provider and then have a service provider accept those authentication tokens for access, rather than requiring the users to create an account on the specific system.
Plan Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC)
Finally, domain 3 discusses business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR). Even though a cloud platform’s inherent redundancy can alleviate many of the common outages that might affect a traditional data center, adequate planning and analysis are still required. Interoperability and portability enable enterprises to use various cloud providers or products within the same cloud provider for BCDR strategies for apps that are totally within a cloud environment. Even applications that are currently hosted in traditional data centers can benefit from cloud services for BCDR, especially since cloud services only charge when they are utilized, eliminating the requirement for standby hardware. The planning stages are critical for implementing proper BCDR methods, but it’s also critical to conduct regular tests to confirm that all components are still acceptable and feasible.
Who is the CCSP for?
The CCSP is intended for IT and information security leaders who are responsible for best practices in cloud security architecture, design, operations, and service orchestration, such as those in the following roles:

CCSP with InfosecTrain
Obtaining a widely respected and recognized industry-standard certification like CCSP will help any IT professional advance in their career. The Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) training course at InfosecTrain will help candidates update and refresh their skills while preparing for the CCSP exam, as well as identify areas where they need to study more. We are a well-known security training organization. Our certified instructors have years of professional knowledge, which they pass on during training. The course will provide you a comprehensive grasp of cloud architecture, infrastructure, deployment models, emerging technologies, and risk management.



 1800-843-7890 (IN)
1800-843-7890 (IN) sales@infosectrain.com
sales@infosectrain.com
 1800-843-7890 (India)
1800-843-7890 (India) 
