Cloud Data Lifecycle
The cloud data lifecycle is a dynamic process encompassing data creation, management, and utilization within cloud computing environments. It begins with generating data from various sources, such as sensors, applications, and users, forming the raw material for subsequent stages. Data is then ingested into cloud infrastructure, which undergoes storage, processing, and analysis. Authorized users and applications access and share this data for insights and decision-making. Over time, data may be archived for long-term storage and regulatory compliance and, ultimately, securely destroyed when it’s no longer needed. This lifecycle framework ensures that data is effectively controlled while maintaining cloud security, compliance, and scalability.

What is Cloud Data Lifecycle?
The cloud data lifecycle encompasses the various phases that a specific piece of data undergoes, starting with its initial creation or capture and concluding with its eventual archival or deletion when it’s no longer needed. It maps out the entire journey that data takes, from its inception to its eventual removal, reflecting the complete spectrum of stages and actions involved in managing data over time. This concept is crucial for organizations to effectively handle and govern their data assets, ensuring they derive maximum value while adhering to data management and compliance requirements.
Different Phases of Cloud Data Lifecycle
1. Data Creation: Data is gathered from various sources, including sensors, devices, applications, human interactions, social media posts, and IoT temperature readings. The raw material for the data lifecycle passes through the ingestion, processing, storage, and analysis phases to produce insightful information. Creating data is the first step in turning unactionable information into knowledge that can be used.
2. Data Storage: Data finds a secure place in cloud storage infrastructure, encompassing object, block, and database storage options. These choices have diverse features to suit various data types and use cases. Cloud storage ensures accessibility, scalability, and resilience while allowing organizations to pick the ideal storage method. This stage is pivotal in the data lifecycle, where data is protected and prepared for future use and retrieval.
3. Data Processing: Processing transforms data into a usable format, making tasks like data analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence applications feasible. This process converts unstructured data into structured data that can power automation and insights. Data processing is essential for deriving value and understanding from data, whether combining numbers for analytics or developing AI algorithms. It bridges the gap between unactionable insight and raw data.
4. Data Sharing: Data is accessible to approved users and programs for collaboration and utilization. This phase entails securely distributing it inside a restricted framework to ensure only authorized parties can interact with the data. Sharing data is crucial to data management as it promotes collaboration, decision-making, and the ability to derive insights from the data. Strong access controls and permissions are needed to maintain data security and compliance.
5. Data Archival: Data is archived to meet compliance requirements and to ensure long-term storage. Data is transferred at this phase to cost-effective, secure storage options built for long-term retention. Archiving ensures that previous data is still available when needed and reduces storage expenses for data utilized less often. It is essential for ensuring data integrity and compliance with legal requirements.
6. Data Deletion: When data no longer serves a purpose or when required by laws and regulations, it is destroyed. Information must be securely deleted or removed at this step to ensure that data cannot be accessed or retrieved. Data deletion is crucial for preserving data privacy and compliance, especially when keeping data is useless or illegal. It adheres to data governance standards and protects sensitive information.
About InfosecTrain
If you are thinking about a career in cloud computing, InfosecTrain offers a variety of training programs designed to provide you with the most current knowledge and skills required in this field. Our courses combine live instructor-led workshops, interactive labs, and self-paced videos to create practical learning experiences. The ability to actively apply their knowledge and participate in hands-on training is given to students by this all-encompassing approach. By completing these courses, participants can gain the skills required for a lucrative career in cloud computing.



 1800-843-7890 (IN)
1800-843-7890 (IN)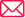 sales@infosectrain.com
sales@infosectrain.com
 1800-843-7890 (India)
1800-843-7890 (India) 
